Stay Ahead of the Curve
Latest AI news, expert analysis, bold opinions, and key trends — delivered to your inbox.
OpenAI’s Custom AI Rewrites the Rules of Cell Reprogramming—50x More Efficient Than Nobel-Winning Method
2 min read OpenAI just helped redesign proteins that turn cells into stem cells—50x more efficiently than the Nobel-winning method from 2012. They built a biology-trained GPT model called GPT-4b Micro. It reversed key signs of aging in cells. AI isn’t just writing poems anymore. It’s rewriting biology. August 25, 2025 13:39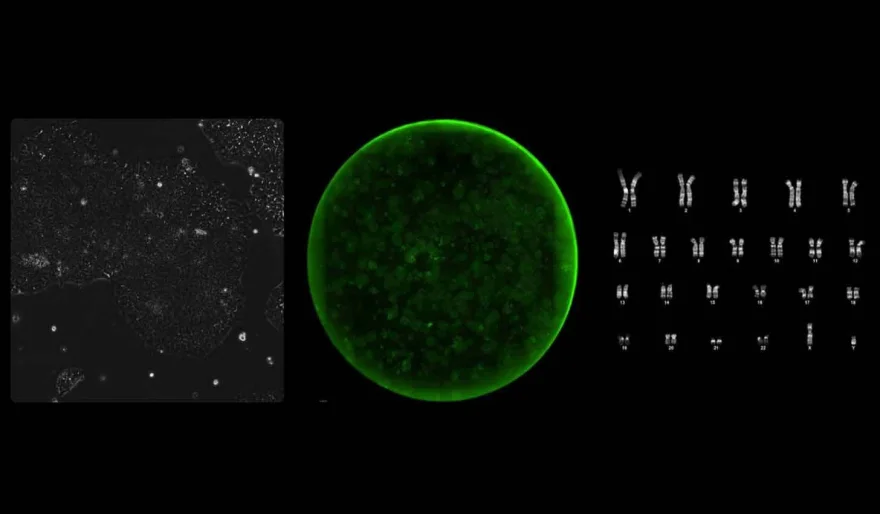
OpenAI just dropped a case study with Retro Biosciences—and it’s wild. Using a custom-built AI model, researchers redesigned the proteins that turn adult cells back into stem cells, achieving 50x greater efficiency than the Nobel Prize–winning approach from 2012.
The science behind it:
-
Researchers created GPT-4b Micro, a custom version of GPT trained specifically on biological data (not internet text), fine-tuned for protein design.
-
The goal? Redesign the Yamanaka factors—a set of proteins known for reprogramming aging cells into stem cells.
-
The result? AI-designed proteins converted cells 50x more efficiently, and showed significantly enhanced DNA repair capabilities.
-
According to the study, the new proteins reversed a key cellular hallmark of aging—and the findings held up across multiple labs and testing methods.
Why this matters:
While public AI models help users write code or summarize articles, domain-specific AI—built by experts for one field—could become a superpower. In biology, chemistry, and materials science, we’re entering a world where decades of lab work collapse into weeks of computation.
The future of science might not just be in labs—it could be in custom AI models trained to rewrite nature’s code.



 AI Agents
AI Agents